ADVT: SMARTWATCHES IN AMAZON
A virus is born, multiplies, spread and on the way, it does some destruction. Let us find out how various viruses behave.
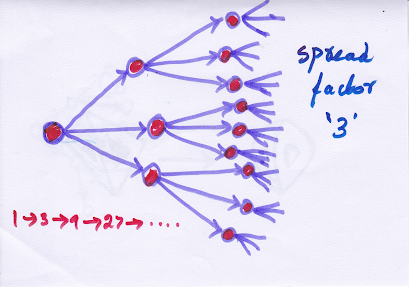
A person with flu may be infectious for five days (infectious period-- I), during which time they will infect about four people (spread factor-- S). One will infect four people, four will infect 16 people. 16 will infect 64 people and so on. Hence 4 is spread factor in the case of flu.
In the following table, various infectious disease, their infectious period, and spread factors are given.
Disease infectious period spread factor
I S
HIV 4 years 3
Smallpox 25 days 4
Flu 5 days 4
Measles 14 days 17
COVID 19 5-15 days more than 1
The key point is that all of the spread factors are greater than 1, making all of the diseases a serious threat if they are left to their own devices. The rate for measles is particularly high, which is why it spreads like wildfire through classrooms of unimmunized children.
We cannot simply multiply the number of infected people and spread factor and tell how many will be affected at the end of a certain period because infection does not happen in an interval of one hour or one day or one week. The infection spread continuously from the start. Hence we have to use a mathematical constant e = 2.71... It takes care of continuous growth. (there is another article on Euler's constant e). So the final formula is,
Number of infected
people after T infectious periods =I.e^(S-1)T
I - initially infected people
S- spread factor
If the spread factor is one, s=1
= Ie^(1-1)T
=Ie^0.T =Ie^0
=I.1
If S=1, then the number of infected carriers remains constant. And if S is more than 1, the infections become an epidemic or even pandemic.
If every carrier can be guaranteed on average to transfer the disease to less than one other person during the whole of their infection period, then the disease will die out. This makes "1" probably the single most important number in the whole of epidemiology.
If the spread factor is 1.5, more than 50 percent of the population will never get the infection. If the spread factor increases the epidemic becomes more pervasive. By the time it reaches 3, only 5% of the population remain uninfected.
Remember, in the case of foot and mouth disease, the spread factor is 100. Once one animal in the farm is affected, the entire farm is declared as affected.
So, contain the spread factor and bring it below one to save people from endemic, epidemic, and pandemic.