In the universe, there are two entities, Life and non-Life. In the physical world, there are two entities, particles and waves.
1. Electron, proton are particles. You and me; table and chair; earth and water; all made of particles.
Sound is the pressure waves; light is the electromagnetic wave. Water wave is the mechanical wave.
2. If force is exerted, particles transport themselves in a straight line. A wave is a disturbance or the energy travelling through a medium or in empty space.
3. A particle cannot deviate from its path without a force. But waves from a source can spread in spherical form in all directions.
4. The energy of the particle is determined by the mass and speed. But the waves energy only depends on its frequency.
Energy = Planck constant *frequency
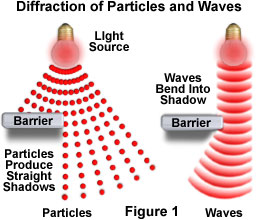
5. The waves can bend over the edges and obstacles and also it can spread through a hole. But particles cannot do so.
6. Waves can be concentrated and made like a solid object. Example: Laser knife.
Particles can be destroyed and disbursed into waves (energy) (E= mc^2 - atom bomb)
7. Waves undergo phenomenon like interference, polarization. But the particles undergo collision, deviation.
8. Some times, waves behave like particles (light photons ). Also particles behave like waves (electron wave). So the border line between the two blurs.
The interplay of matter and waves keep this universe live.