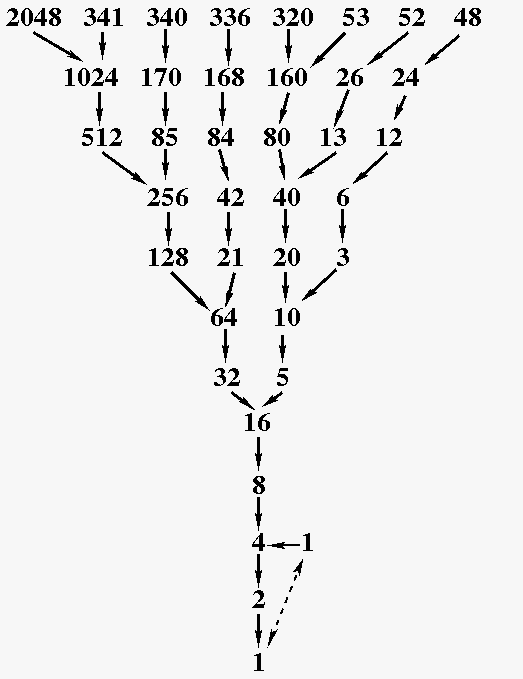We will produce a sequence of numbers following some rules.
1. Take any positive natural integer.
2. If it is even, next term will be half of it.
3. If it is odd, multiply it by three and add one to get next term.
4. Apply the rule no.2 or 3 to the next term and go on produce the sequence.
Let us take an example; consider the number 12. It is even; hence next term is 6, again even; next term is 3. Now it is odd; next term is 3+3+1 = 10. Just proceed like this, we get,
12, 6,3,10,5,16,8,4,2,1
Now let us take 19;
19,58,29,88,44,22,11,34,17,52,26,13,40,20,10,5,16,8,4,2,1
It seems, we always end up with 8,4,2,1. In fact, all the numbers tested so far (even using the computer) always end up with 8,4,2,1... In other words, this sequence ultimately reaches one.
We know, it is impossible to test the infinite numbers. Is there any mathematical proof that the sequence will always reach one? No, not so far. This problem is called "Collatz conjecture" (assumption). This problem can be easily understood by a 10-year-old. But the mathematics world has not solved the problem even today.
One great mathematician once said, "mathematics is not ready for such problems."
One can easily a write small computer program to produce this sequence. This problem has not practically served any purpose so far. But it can attract youngsters towards mathematics and number theory. Some people say, the solution to the problem carries some prize money. But, remember there is no easy solution to this problem. Anyway, attempt it.
Philosophically, we may arrive at one conclusion. That is, " Even if you multiply something three times, and spend half of it, you will end up with one unit". Is the nature trying to tell us something through Colletz conjecture?
Note;
The stopping time or number of steps to arrive at one does not follow any pattern. It baffles us more. A small computer program to produce the sequence is given here.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------