We know, the flow of electrons is electric current. Electrons are said to be negative charge carriers.
In a molecular structure, if there is a vacancy for an electron, it is called hole. When an electron from somewhere in the structure fills-up this hole, a new hole will be created where the electron has just left. Hence a hole can move opposite to the electron. So the holes are said to be positive charge carriers.
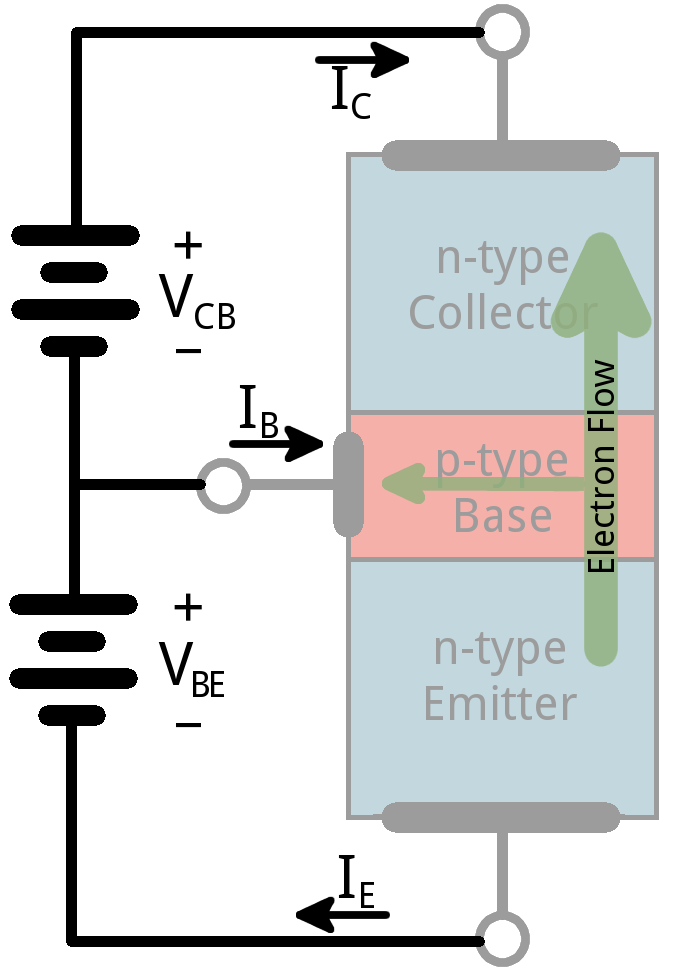
In a germanium crystal, arsenic is infused. We get electron rich material called N type (negative) material. When boron is added to germanium, we get holes surplus P type (positive) substance.
A thin P type material is sandwiched between two N type material. Now a transistor is made. These three pieces NPN are respectively called emitter, base, and collector.
By connecting negative of the battery to the emitter(N) and positive to the collector(N), the electrons can be pushed from emitter and pulled at the collector. On the way, through the base(P) some electrons combine with holes. So some electrons are lost in the base. But most of the electrons reach collector resulting in collector current.
By applying suitable negative voltage to the base, we can control the quantity of holes in the base region. consequently the loss of electrons flowing through the base and the collector current is also controlled.
In a nutshell: By varying small voltage that is applied to the base, one can produce big variations in the collector current. This is amplification, main function of transistor.
Example of one application: Microphone(mic) converts voice into electrical signals. These small varying electric voltage is fed to the base of the transistor. Then we get large varying current as output from the collector. It is then supplied to a speaker which produces big sound.
So many transistors are present in all the electronic gadgets. In the CPU of the computer, millions of transistors is present.
At present : No transistor, no electronics.
Note: PNP transistor is also possible.